Blog
Articles to grow your career
Article
Selection sort – Coding algorithms for interview
Here is another sorting option “Selection sorting”.
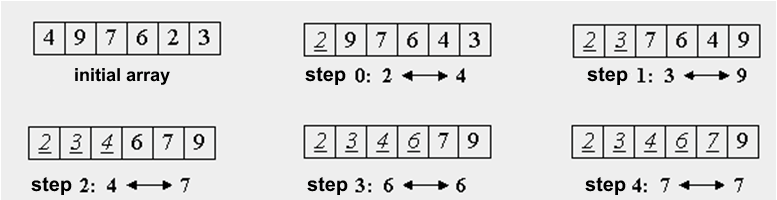
The idea of the algorithm is that we are looking for the minimum element in the array and swapping it with the element in position zero. Next, look for the next largest element and swap it with the element at index 1, and so on:
Consider the implementation of the algorithm. The outer for loop is responsible for the pass number, and the inner one is responsible for finding the minimum value in the current pass. Please note that in the inner loop, we do not start searching for the minimum element from the very beginning, but skip the elements already found in the previous step:
Do you want to join us?
Leave an application and get a free consultation from our manager.
- Help in choosing a direction
- Course consultation
- Additional materials for the start
public class SelectionSorter {
public static void sort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { // i - number of the current iteration
int pos = i;
int min = array[i];
// loop - selection of min element
for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[j] < min) {
pos = j; // pos - index of the min element
min = array[j];
}
}
array[pos] = array[i];
array[i] = min; // swap places min with array[i]
}
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectionSorterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] data = {
{},
{1},
{0, 3, 2, 1},
{4, 3, 2, 1, 0},
{6, 8, 3, 123, 5, 4, 1, 2, 0, 9, 7},
};
for (int[] arr : data) {
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(arr) + " => ");
SelectionSorter.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}