Blog
Articles to grow your career
Article
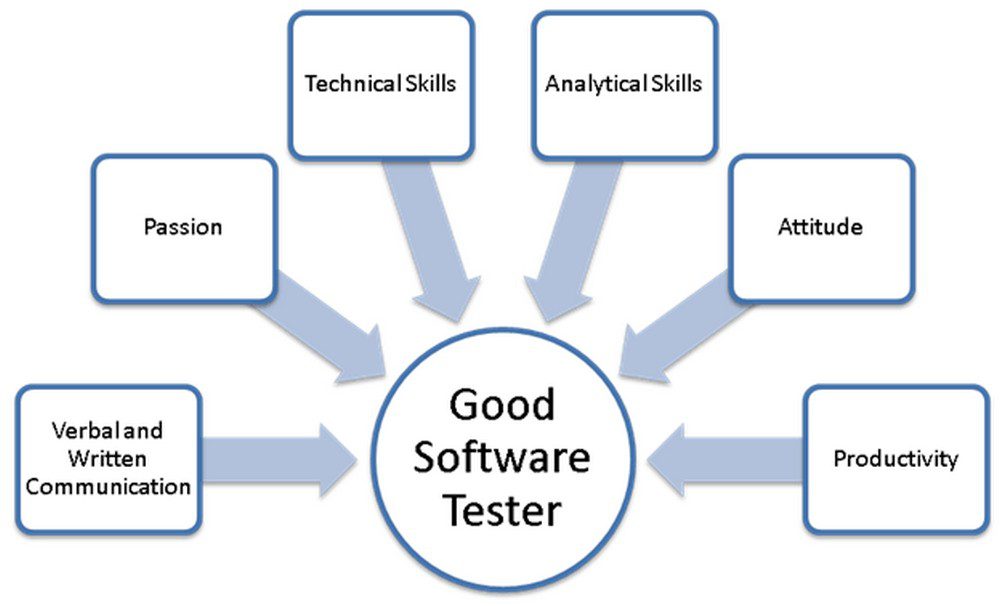
Key Skills Required for a Career in Quality Assurance Testing
Customers seek bug-free products and seamless, efficient applications, and software testers strive to achieve that objective. The primary responsibility of QA testers is to ensure thorough testing and the absence of application defects by using both Manual QA and Automated QA Testing solutions. Becoming a successful QA tester is challenging; it requires a high level of responsibility and resilience. Here are the key skills required for a career in quality assurance testing
What Does A QA Manager Do?
A QA manager, tester, engineer, or software quality assurance analyst is accountable for analyzing and inspecting modified applications to ensure their proper functionality. Their primary objective is identifying and eliminating potential issues and delivering exceptional software and bug-free applications that provide an optimal user experience.
In addition, QA testers also oversee the design phase, proactively identifying problems with software applications before they become major concerns. They serve as intermediaries between industries developer, clients, and QA teams, improving the development process.
The Skills That Can Set You Apart from Others
Effective Communication
Contrary to popular belief, effective communication skills are essential for QA testers, even in their interactions with C-level executives and stakeholders. While some may perceive the role as isolated, software testers must communicate effectively with clients and individuals outside their immediate responsibilities, particularly when addressing technology development issues. The ability to engage with both technical and non-technical individuals is crucial.
Strong Programming Skills
Given the significance of test Automation in QA testing, QA engineers must possess a solid understanding of tech programming languages to excel in their roles. Proficiency in programming languages like Java, Python, C#, or Ruby is necessary for implementing UI test automation and scripting automated tests. Such skills facilitate productive communication between QA tech engineers and software developers regarding the product.
Efficient Time Management
Time constraints are common in QA testing, and mastering the art of estimating, prioritizing, and planning testing activities is vital. These skills help QA professionals avoid stressful situations and enable effective team collaboration.
Pinpointed Data Visualization
QA managers must be able to visualize data effectively for improved debugging in advance. Understanding the client’s specifications enables QA testers to visualize real-time business scenarios. QA managers should share this information with the team or higher management if issues arise. Following a system simulation, they should organize the delivery sequence accordingly.
Do you want to join us?
Leave an application and get a free consultation from our manager.
- Help in choosing a direction
- Course consultation
- Additional materials for the start
Problem-Solving Skills
The role of a QA engineer involves solving complex technical problems. QA professionals must address software testing challenges and effectively manage issues that arise. Each new problem requires a unique, intelligent, and efficient approach to resolution. The ability to develop innovative solutions for technically intricate issues is a valuable trait to seek as a QA engineer.
Analytical Prioritization
In the fast-paced environment of QA and technology, multiple tasks may be ongoing simultaneously. Knowing which tasks require immediate attention and completion are essential tips to prevent confusion and the need for redoing tasks. Proper prioritization tips help maintain organization and efficiency.
Conduct Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing is an approach that combines test design, simultaneous learning, and execution of a software’s code. It relies on the tester’s expertise to uncover flaws that may not be easily detected through conventional testing methods. This approach aims to expose hidden vulnerabilities and ensure thorough software evaluation.
Cross-Team Sync
A successful QA manager thrives on effective teamwork. Their role involves organizing the team’s workflow to ensure timely project delivery. It is crucial to consistently motivate the team, particularly the product development team, to go above and beyond expectations. Encourage your team to arrange hackathons and other events that facilitate task completion.
Agile Mindset
Familiarity with the Agile process model is essential for every QA manager. This approach to software development emphasizes iterative development. In Agile processes, tasks are broken down into smaller iterations without long-term planning. The focus lies on requirements and scope at the beginning of each development stage. The number of iterations, their duration, and their range are predetermined.
Peer-to-Peer Approach
The peer-to-peer approach is a crucial skill for a competent QA manager. A customer service team uses this method to evaluate their team members’ performance using a quality assurance scorecard. By identifying weak links and working on improvements, timely delivery is ensured. As a skilled QA manager, you can establish similar processes to accelerate product release velocity.

Quality management with QA (assurance), QC (control) and improvement. Standardisation and certification concept. Compliance to regulations and standards. Manager or auditor working on computer.
Conclusion
If you aspire to venture into the realm of quality assurance or desire to improve your QA tester’s CV, possessing strong skills in quality assurance is essential.
What next? If you think a career in Quality Assurance is for you, contact Spincareer for more information or check out our manual and automation QA courses!